Ether is the second most popular currency after Bitcoin.Encryption CurrencyBut it's more than just a digital currency. As an open-source blockchain platform, Ether supports smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps), laying the groundwork for innovation in areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), NFT, and more.
This guide takes a deep dive into the history of Ethernet, how it works, its strengths and weaknesses, and what's in store for the future, giving you a comprehensive look at this game-changing blockchain technology.
- Decentralized blockchain platform with support for smart contracts and dApps.
- The native cryptocurrency is Ether (ETH).
- Critical Innovation: Smart Contracts, Ethernet Virtual Machine (EVM).
- The consensus mechanism: Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Apply: DeFi, NFT, Gaming, Supply Chain Management.
- Advantages: Decentralized, programmable, and sustainable.
- Disadvantages: Expansion challenges, high transaction costs, price volatility.
- Future: The Ethernet 2.0 upgrade will increase scalability and sustainability and unlock even more possibilities.
What is Ether (ETH)?
Ethereum (ETH) also known asEtherIt is a decentralized, open source and blockchain-based contract management platform with smart contract features.
The definition of "Ether" usually refers to the blockchain technology, while Ether (ETH) is the blockchain's native cryptocurrency, which can be used for both online transactions and trading on exchanges.
Launched in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin and a team of developers, Ethereum is the second blockchain or decentralized ledger technology (DLT) network and its associated cryptocurrencies to officially go online, following Bitcoin in 2009.
Ethernet's goal is to provide a platform for decentralized applications (dApps) based on smart contracts with no downtime, no fraud, and no third-party interference.
Ether was the first alternative currency (altcoin) to Bitcoin and remains the largest alternative currency by market capitalization.
Techopedia explains the meaning of Ether (ETH)

The Ethereum blockchain is developed and supported by the Ethereum Foundation, a Swiss non-profit organization. The Ethereum Foundation documents various types of ongoing projects on its website.
Ethernet supports programs developed in languages such as C++, Python and Java, making it easy for open source developers to build applications on the platform.
Smart contracts are self-executing protocols whose terms are written directly into the Ethernet code, meaning they are automatically executed when predefined conditions are met and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Developers can apply these smart contracts to decentralized applications (dApps) to facilitate peer-to-peer (P2P) on-chain transactions, structured contracts, customer loyalty systems, specific types of financial transactions, and crowd-funding programs.
History of Ether
The origins of ethereum can be traced back to 2013, when cryptocurrency enthusiast Vitalik Buterin floated the idea of a new blockchain platform in a white paper.
Butlin envisioned a decentralized platform that could support more complex applications than simple transactions to address some of the limitations of the Bitcoin blockchain.
In 2014, Buterin, along with a group of co-founders including Gavin Wood, who would later create the Polkadot and Kusama blockchains, Charles Hoskinson, who would later create the Cardano blockchain, and Joseph Lubin, formally announced the Ether project.
They held a crowd-funding campaign known as an Initial Token Offering (ICO) and raised over $18 million through the sale of ETH tokens.
This funding enabled them to kick off development of the project, and the Ethernet network went live on July 30, 2015 with the launch of its first version, Frontier.
This marked the beginning of a new era in blockchain technology, as Ether introduced the concept of smart contracts. Soon after its launch, Ether quickly caught the attention of developers, entrepreneurs and the wider cryptocurrency community.
Its flexibility and programmability have attracted innovators who see the potential to build dApps that cover a wide range of industries, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, gaming, and more.
Since then, Ether has undergone several upgrades to improve its scalability, security, and functionality. One of the most important milestones in the history of Ether is the ongoing transition to Ether 2.0, paving the way for the next phase of Ether's development.
EtherlandsMode of Operation
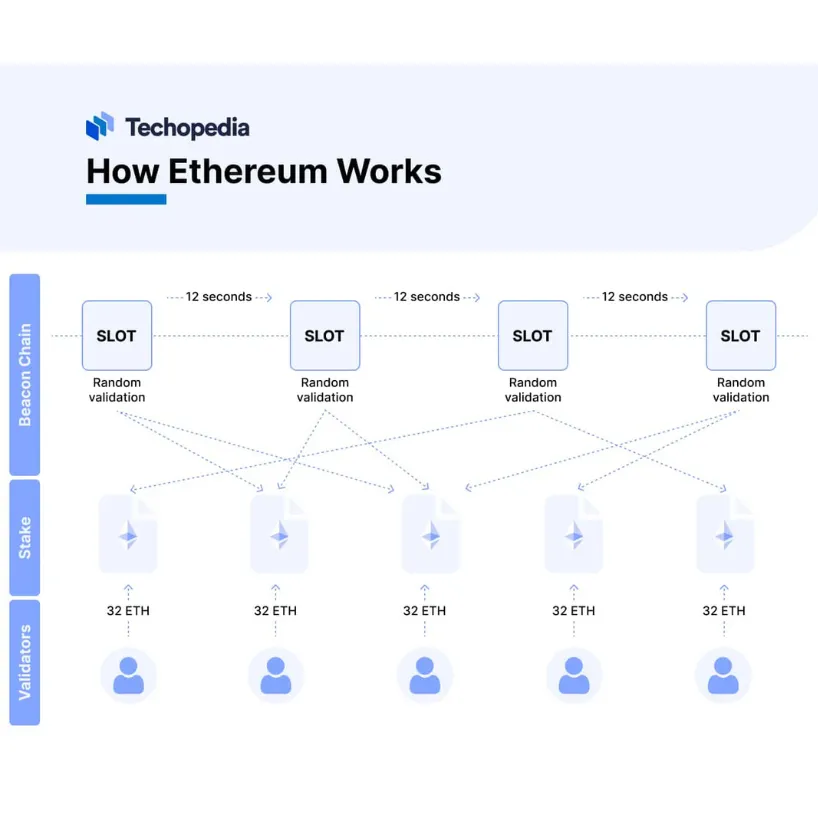
The Ethernet blockchain runs on a decentralized network of computers called nodes that work together to keep the network running.
These nodes store the entire Ethernet blockchain, validate transactions, and execute smart contracts.Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) This is the environment in which smart contracts are executed.
Ethereum initially used the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, but after the 2022As part of the Ether 2.0 upgrade, a process known as the The Merge The transition to the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism was made.
In Ether 2.0, pledging replaced the traditional mining process in PoW. In PoS, verifiers are selected based on the amount of Ether (ETH) they pledge or lock on the blockchain as collateral.
This mechanism incentivizes verifiers to act honestly and follow the rules of the network. When a user initiates a transaction or interacts with a smart contract on the Ethernet network, the transaction is broadcast to all nodes in the network.
Validation Nodes are selected based on their pledge volume and other criteria determined by the Agreement to propose and validate blocks. The selected node validates the transaction, including checking its authenticity, ensuring that the sender is adequately funded, and confirming that the transaction complies with the rules of the Ethernet Protocol.
The verifier creates a new block containing multiple transactions and broadcasts it to the network. Other verifiers in the network confirm the validity of the block by examining the transactions, making sure they comply with the rules of the Ethernet protocol, and verifying cryptographic signatures.
The verifier acknowledges the validity of the block by attaching his or her signature.
After a certain number of validators have recognized the validity of a block, the block is finalized, meaning it is added to the Ethernet blockchain and cannot be tampered with.
Verifiers are rewarded for successfully proposing and endorsing blocks, while those who act maliciously or try to manipulate the network may be penalized by deducting a portion of their pledge.
A verifier may exit the pledging process and withdraw their pledge after a certain period of time, usually after a specified number of blocks have been verified.
Upon exiting the pledging process, the Verifier may retrieve his/her pledged Ether as well as any accrued rewards.
How Smart Contracts Operate
Smart contracts are stored on the Ethernet blockchain and are automatically executed when a predefined condition is met. Developers can use Ethernet's native programming language. Solidity or other compatible language such as Vyper Write smart contracts.
Once deployed on the Ethernet network, smart contracts are tamper-proof and tamper-resistant, providing a trustless and transparent way to conduct transactions that does not rely on intermediaries.
What is Ether 2.0?
Ether 2.0 is a major upgrade for the Ether blockchain, which was launched on 2020Launched to enhance the network's scalability, security and environmental friendliness, it aims to unleash the new potential of decentralized applications (dApps) and accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology across industries.
The transition to PoS has been envisioned from the beginning of the Ethernet development roadmap, as Buterin had long foreseen the need for the network to improve its scalability and energy efficiency.
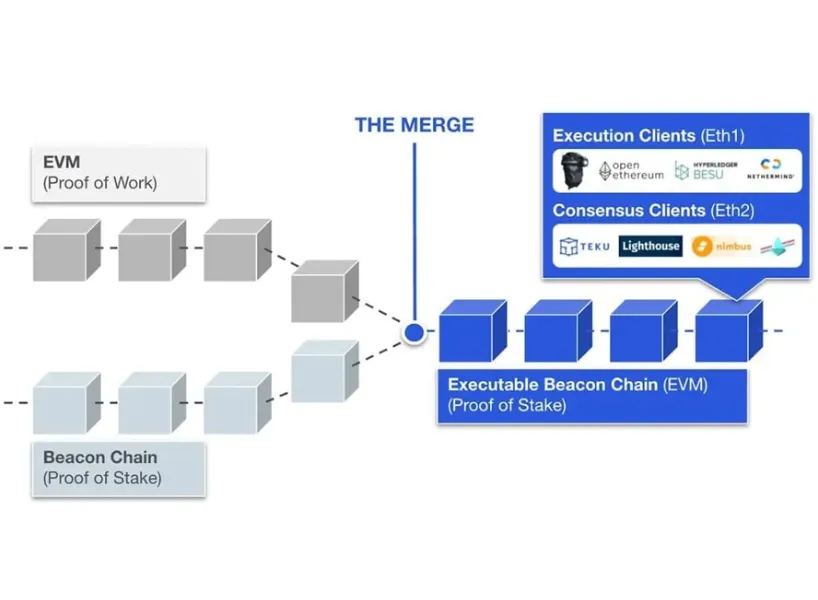
This upgrade introduces several key features, including:
Proof of Interest
Ethernet 2.0 replaces the PoW consensus mechanism with PoS. This is accomplished by The Merge Conversion of September 2022This marks an important milestone in the development of Ethernet as it reduces energy consumption and enhances the security and scalability of the network.
slice
Ethernet 2.0 implements sharding, which breaks up the blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces called shards. Each shard can process transactions and execute smart contracts independently, allowing transactions to be processed in parallel and significantly increasing network throughput.
Beacon Chain
The Beacon Chain is the backbone of Ethernet 2.0, coordinating verifiers, managing PoS consensus mechanisms, and facilitating communication between shards. It lays the foundation for future upgrades and improvements to the Ethernet network.
cross-slice communication
Ethernet 2.0 introduces a mechanism that allows tiles to seamlessly interact and share data with each other. This enables complex transactions and applications across multiple tiles, increasing Ethernet's capabilities and unlocking new use cases.
Status Execution and Transition Functions
Ethernet 2.0 enhances state execution and transition capabilities that govern how transactions are processed, how state changes are applied, and how consensus is reached within the network. The goal is to improve performance, reduce latency, and minimize transaction costs for users and developers.
Ether Mining
With the upgrade to Ether 2.0, the blockchain shifted from mining as a way to validate transactions and reward participants to staking. Staking provides a more efficient and environmentally friendly alternative while ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain.
Verifiers play a key role by proposing and verifying blocks, and their participation is critical to the smooth operation of the Ethernet PoS consensus mechanism.
Energy Consumption in Ethernet
Reducing the energy consumption of running blockchain nodes is one of the key drivers of the transition from PoW to PoS in order to make it more environmentally sustainable.
According to a study by the Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (CCAF), theThe Merge After that, Ether's GHG emissions dropped by about 20%. 99.97%Estimates before the merger 10.3 million tons of CO2e drop to 2,800 tons CO2eThe
This change occurs in the context of a significant increase in the number of Ethernet beacon nodes. In addition, CCAF estimates that about 48% For sustainable energy (32% Renewable Energy, 16% Nuclear Energy), of which 12% For wind energy.
Compare the difference between Ether and Bitcoin.
As the top two cryptocurrencies, they are often compared by cryptocurrency observers and novices alike. While both are based on blockchain technology and share some similarities, they are fundamentally different in their purpose, functionality and capabilities, and play different roles in the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Below is a complete translation of the form, with the key points highlighted according to your requirements and presented in a tabular format:
| perspective | Ethereum | Bitcoin |
|---|---|---|
| Release Date | July 30, 2015 | January 3, 2009 |
| Founder | Vitalik Buterin, Gavin Wood et al. | Satoshi Nakamoto (pseudonym) |
| goal | A Platform for Decentralized Applications (dApps) and Smart Contracts | Digital currency; a store of value used primarily for financial transactions |
| consensus mechanism | Transition from Proof of Workload (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) | Proof of Workload (PoW) |
| Block Time | Approx. 13-15 seconds | About 10 minutes |
| Transaction speed | Higher throughput to process more transactions per second | Lower throughput, limited scalability |
| Transaction Fee | Variable, subject to network activity | Variable, affected by network congestion |
| Supply Limit | No fixed supply, but issue rate decreases over time | Limited to 21 million pieces, with new supply halved every four years (halving mechanism) |
| Currency Policy | Flexible issuance, network upgrades could lead to inflation | Ventilator, Fixed Supply |
| Intelligent Contract | Support to enable programmable transactions and decentralized applications (dApps) | No support, limited script language functionality |
| Application Scenarios | Decentralized Finance (DeFi), Gaming, NFT, Supply Chain Management | Digital gold, cross-border remittances, store of value |
| social grouping | Large and active developer community | Strong and stable user base |
| Environmental Impact | Proof-of-Statement (PoS) Transition Dramatically Reduces Energy Consumption | Criticized for high energy consumption of Proof of Work (PoW) |
Pros and Cons of Ether
Advantages
- Decentralized Intelligent Contracting Platform
- Sustainability
- interoperability (of communications equipment)
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Reducing Environmental Impacts
- Ecosystem
- decentralized governance
- Privacy
Disadvantages
- Scalability Challenges
- High Transaction Fees
- Price volatility
- Security Risks
- Interoperability Challenge
- Adoption Barriers
- Difficulty in coordinating promotion
- Competitive Market Environment
Is Ether safe?
Blockchain networks like ethereum run on theDecentralized Node NetworkawayLess susceptible to single points of failure and scrutinyThis is designed to ensure that no single entity can control the entire network, thereby increasing security and resistance to attacks. This is designed to ensure that no single entity can control the entire network, thereby increasing security and resistance to attacks. Ethernet relies onencryption algorithmto protect transactions, validate blocks, and protect user privacy. Once a transaction is included in a block and validated by other blocks, theAlmost impossible to alter or reverseThe
Ethernet on theSmart contracts are audited and tested for securityIn order to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities, although errors or bugs may still exist in the code. To address this issue, the ecosystem is implemented via theVulnerability Rewards Program and FundingTo incentivize security research and vulnerability capture and encourage researchers to identify and report vulnerabilities.
EtherCast also conducts regularNetwork Upgrades and ImprovementsThe company's first step was to develop a new software program to address security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and introduce new features.
The goal of the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism is to make it prohibitively expensive for malicious attackers to create blocks. Ethernet requires users toPledge 32 ETH as a validation nodeIf fraudulent behavior is detected, it will beslashing - destroying part or all of the pledged ETHThe
The Future of Ether
The Future of EtherFull of hopeOur ongoing development efforts are focused onScalability, Sustainability and InteroperabilityThese improvements are expected to unlock new possibilities for the network and drive further adoption of decentralized applications.
Most emerging cryptocurrency projects use the Ether blockchain, which plays an important role in the future direction of the Ether price.
Extended Reading:Ethernet Price Forecasts for 2024, 2025, 2030
Conclusion
Ether is aConstantly Innovating Blockchain PlatformsIt supports decentralized applications and smart contracts. With continued development and community support, EthernetIt is expected to play an important role in the future of finance, technology and other fieldsThe
Ether Frequently Asked Questions
Simply put, what is Ether?
Ether (Ethereum) is aDecentralized Blockchain PlatformIt allows developers to construct and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) without relying on intermediaries.
Why is Ether so valuable?
The value of ethereum is its ability to supportDecentralized Applications (dApps) and Smart ContractsThese technologies have potential.Subverting Traditional Industries(e.g. finance and gaming) and createNew Economic OpportunitiesThe
What will Ether be worth by 2030?
Predicting the future value of cryptocurrencies like ethereum has aopportunisticand is subject toAdoption, Regulatory Developments and Technological AdvancesThe impacts of various factors such as
Is ETH a good investment option?
As with any investment, investing in Ether (ETH) has itsRisksWhen making an investment, it is important to be sure that you have a good idea of what you are doing. When investing, it is important toThorough ResearchConsider the following factors: your risk tolerance, investment objectives, and the volatility of the cryptocurrency market.
Is Ether better than Bitcoin?
Ether and Bitcoin haveDifferent FeaturesIt is designed toRealization of different usesBitcoin is primarily regarded as a Bitcoin is primarily viewed asDigital Value Storage ToolsEther provides a platform for developers to build onExecution of Smart Contractsto build decentralized applications. Both have their ownUnique advantages and application scenariosThe