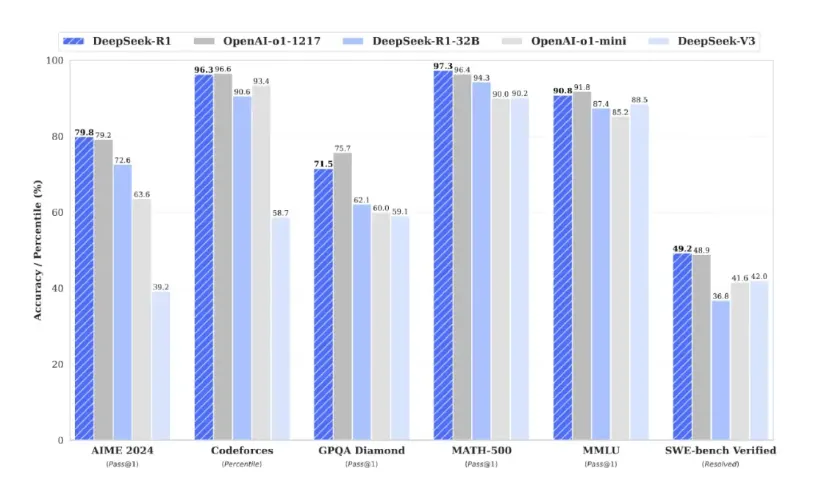
DeepSeek Stick to the open source route, intensively update MoE+, inference, and multimodal models. Recently, DeepSeek has released and open-sourced a number of large models, and its low-cost and high-efficiency features have quickly attracted the attention of users around the world.
Among them, DeepSeek-V3 released on December 26, 2024 is a self-developed MoE model with 671B parameters, which only needs to activate 37B when running, and pre-training on the data of 14.8T tokens; and DeepSeek-R1 launched on January 20, 2025 marks a major breakthrough in user mind distillation technology.
On January 27th, DeepSeek uploaded the vision model Janus-Pro+ and the multimodal understanding model JanusFlow+-1.3B on the Hugging Face+ platform, further expanding applications in the imaging field.
This guide.TechdukerIt will focus on the core questions of "What is DeepSeek, what can DeepSeek do, and how to use DeepSeek? How to use DeepSeek?" and other core questions are analyzed to help users better understand and apply the technology.
What is DeepSeek?

DeepSeek is a company that specializes inGeneralized Artificial Intelligence (AGI) DeepSeek-R1 is a Chinese tech company that researches and develops large-scale AI models, and DeepSeek-R1 is its open-source inference model that is capable of handling a wide range of complex tasks and is free for commercial use.
The DeepSeek Advantage
- AI Technology Leadership: Provides powerful natural language processing capabilities for a wide range of application scenarios.
- Free and Open Source: Open it up to individuals and businesses, and lower the technology threshold.
- Strong reasoning skills: Solve complex problems and support logical reasoning and deep thinking.
- Continuous Updates: Continuously optimize model performance to improve accuracy and intelligence.
Extended Reading:What is DeepSeek? China's New AI Powerhouse: Technology Innovation or Plagiarism?
What can DeepSeek do?
Directly facing the user or supporting the developer, it provides intelligent dialog, text generation, semantic understanding, computational reasoning, code generation and supplementation and other application scenarios, supports Internet search and deep thinking mode, and also supports document uploading, which is able to scan and read the text content in all kinds of documents and pictures.
Below is an introduction of its core functions.
Intelligent Dialogue and Text Generation
- Text Creation: Writing articles, stories, poetry, marketing copy, social media posts, scripts or dialogue design.
- Abstracting and Rewriting: Generation of long abstracts (papers, reports), text simplification (reducing complexity), multilingual translation.
- Structured OutputAutomatic generation of forms, lists (e.g., schedules, recipes), code annotations, and document authoring.
Natural Language Understanding and Analysis
- Semantic Analysis
- Sentiment analysis (comments, feedback)
- Idea Recognition (Customer Service Dialog, User Inquiry)
- Entity Extraction (Person, Place, Event)
- Text Classification
- Theme tag generation (e.g. News category)
- Garbage Content Inspection
- Intellectual reasoning
- Logical Problem Solving (Mathematics, Common Sense Reasoning)
- Causal analysis (event correlation)
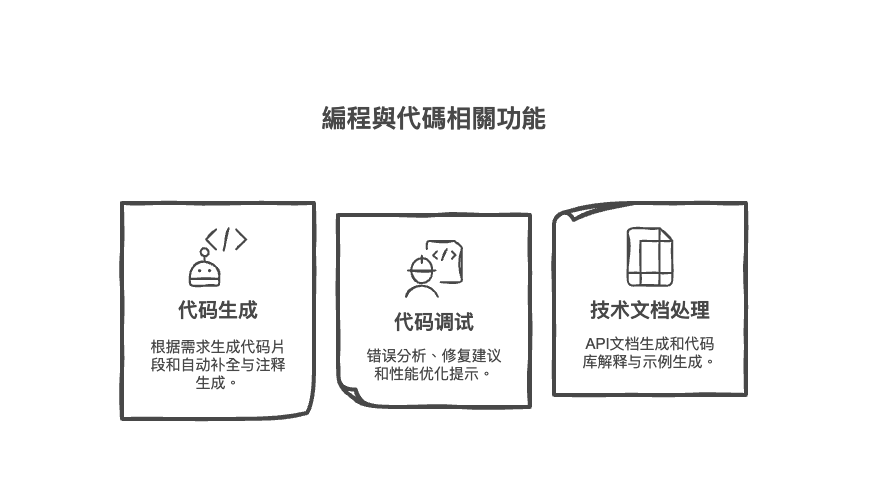
Programming and code-related functions
- Code generation
- Generate code snippets based on requirements (Python, JavaScript)
- Auto-completion and annotation generation
- Code debugging
- Bug Analysis and Fixing Suggestions
- Code Performance Optimization Tips
- Technical Documentation
- API Document Generation
- Codebase Explanation and Example Generation
In addition, DeepSeek supports Web Search, Deep Thinking Mode, File Upload and Image Text RecognitionThis will further enhance the user experience.
How do I use DeepSeek?
- Visit the DeepSeek website to register or log in.
- Enter the chat interface, type in a question or request, and the AI will respond accordingly.
- If you need to generate a specific type of content (e.g., code, articles, summaries, etc.), you can directly enter the relevant command.
- Note that DeepSeek is dependent on By July 2024 The knowledge provided in the response is not currently supported for real-time web searching.
How do you go from beginner to master?
AI tools are becoming more and more popular, and how to utilize them more effectively will be the key to improving one's competitiveness. Here are a few suggestions for learning:
- Learn to ask precise questions: Using specific, clear questions will result in more accurate responses.
- Familiarity with AI limitations: Understand the benefits and limitations of DeepSeek to avoid inappropriate usage scenarios.
- Practice more, test more: Explore the many ways in which AI can be applied through hands-on experience.
- Combining other tools: Integrate DeepSeek with your workflow to increase efficiency and creativity.
Comparison of AI Inference Models and Generalized Models
AI models have their own strengths in different application scenarios, with inference models specializing in mathematical reasoning and logical analysis, and general-purpose models more suitable for text understanding and generation. The following is a detailed comparison of their characteristics and application areas.
Large Models of Reasoning (for Logical Analysis and Mathematical Reasoning)
Reasoning macromodels are models that are able to enhance their reasoning, logical analysis, and decision-making capabilities over traditional macromodels. They are usually equipped with additional techniques such as reinforcement learning, neural symbolic reasoning, meta-learning, etc. to enhance their reasoning and problem solving capabilities.
Typical example:
- DeepSeek-R1, GPT-o3: Excellent in mathematical reasoning, logical reasoning, code generation, and real-time problem solving.
Non-inferential macromodeling (for text generation and comprehension)
Applicable to most tasks, non-referential macromodels generally focus on language generation, context understanding and natural language processing without emphasizing deep reasoning capabilities.
This type of model is usually trained on large amounts of textual data to master linguistic patterns and be able to generate appropriate content, but it lacks the complex reasoning and decision-making capabilities of an inference model.
Typical example:
- GPT-3, GPT-4 (OpenAI), BERT (Google)The main applications are language generation, language understanding, text categorization, translation, and other scenarios.
.webp)
| Classification Standards | inference model | inferenceModels (generic models) |
|---|---|---|
| Areas of Strength | Mathematical derivation, logical analysis, code generation, and complex problem solving. | Text Generation, Creative Writing, Multi-Round Dialogue, Open-Ended Q&A |
| Areas of disadvantage | Diffuse tasks (e.g., poetry writing) | Tasks requiring strict logical chains (e.g., mathematical proofs) |
| Performance Nature | Specialized in logic-dense tasks | Specializes in missions with high diversity |
| Strength and Weakness Determination | Not better across the board, but only significantly better in the areas they are trained to target. | Generalized scenarios are more flexible, but tasks rely on cue control. |
AI Model Performance and Application Scenarios: Fast Thinking and Slow Thinking Models
AI models can be categorized according to their reasoning style asFAST THINKING MODEL (probabilistic forecasting) respond in singingSlow Thought Patterns (Chained Reasoning)Both have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios.
1. Performance and Computing Principles
- FAST THINKING MODEL (probabilistic forecasting) → as ChatGPT 4.0Relying onprobabilistic modelIn addition, through the training of a large number of dataQuick Prediction AnswersApplicable toImmediate response and efficient handlingThe
- Slow Thought Patterns (Chained Reasoning) → as OpenAI o1Based on CoT (Chain-of-Thought)The step-by-step reasoning problem applies to each of the steps in theComplex Decision Making and Logical AnalysisThe
2. Competency Comparison
| Comparison | Faster Thinking Mode (ChatGPT 4.0) | Slow Thinking Mode (OpenAI o1) |
|---|---|---|
| Sexual energy performance | Fast response time and low computational cost | Slow thinking and high computational costs |
| algorithmic principle | Based on probabilistic prediction, fast prediction of possible answers by training on a large amount of data | Based on Chain-of-Thought, reasoning step-by-step through each step of a problem to arrive at an answer. |
| Decision-making ability | Rely on default algorithms and rules for decision making | Ability to analyze situations and make real-time decisions on your own |
| Creativity | Limited to pattern recognition and optimization, lack of real innovation capability | Ability to generate new ideas and solutions, with the ability to innovate |
| Human-machine Interaction | It is more difficult to understand human emotions and intentions according to the pre-scripted responses | Interacts more naturally with people and understands complex emotions and intentions |
| Problem solving skills | Specialized in solving structured and well-defined problems | Ability to tackle multi-dimensional and unstructured problems and provide creative solutions |
| Ethical Issues | As a controlled tool, there are few ethical issues. | Generating Ethical Discussions on Autonomy and Control Issues |
The emergence of CoT Chain Thinking divides the big models into two categories: "probabilistic prediction (fast reaction)" models and "chain reasoning (slow thinking)" models. The former is suitable for quick reaction and immediate tasks, while the latter solves complex problems through reasoning. Understanding their differences will help you choose the right model for different scenarios and achieve the best results.
3. Application Scenarios
- Faster Thinking Mode (ChatGPT 4.0) applies:
- Real-time response and efficient processing
- Open Dialogue
- Simple Question Answer
- Standardized text output (e.g., product descriptions)
- Slow Thinking mode (OpenAI o1) applies:
- Complex Reasoning and Decision Making Tasks
- In-depth analysis and logical reasoning
- Data Reasoning and Planning
- Scenarios requiring precise decision making (e.g., financial analysis, legal reasoning)
AI Cueing Strategy Differences
This section highlightsinference modelanduniversal modelDifferent strategies in cue design.
1. Reasoning models
- Cues are concise and to the point because of the reasoning logic built into the model.
- Instead of disassembling the problem step-by-step, the model automatically generates structured reasoning. Avoid additional interference (e.g., forcing steps to be disassembled may reduce model performance).
2. Generalized models
- Need to show guided reasoning steps (e.g., CoT hints), otherwise critical logic may be skipped.
- Need to fill in gaps in modeling and reasoning skills (e.g., require step-by-step thinking, examples).
- Avoid over-trust and ensure reliability through multiple rounds of validation.
Key Principles of AI Use
Advances in AI have allowed us to quickly tackle a wide range of tasks, but the key to realizing their value is to use them correctly. Here's a look at model selection, cue design, and error avoidance to help you utilize AI tools more efficiently.
1. Model Selection
Different AI models are suitable for different tasks, and choosing the right model can improve accuracy:
- Mathematics, Logical Reasoning Tasks → Choose a model with enhanced reasoning capabilities [e.g., GPT-4 Turbo with CoT (Chain Reasoning) or other reasoning-optimized AI].
- Text Generation, Translation, Dialogue Tasks → Selecting a Common Language Model[e.g. GPT-4].
2. Cue Design
Well-designed cues allow AI to perform at its best:
- inference model: UseConcise InstructionsThe goal is to focus on the target and trust its internalized power. ("Just say what you want").
- universal model: AdoptionStructured, compensatory guidance("Make up for what's missing").
3. Avoid Mistakes
Avoid common errors and improve the reliability of AI applications:
- inference model: Don't use "starter" prompts (e.g., role-playing) that may interfere with their logical thread.
- universal model: Don't "over-trust" generic models (e.g., ask complex inference questions directly, need to validate results step-by-step).
From giving orders to expressing needs
When interacting with an AI, the clarity of your commands will directly affect the quality of the AI's response. Different command strategies are suitable for different situations, and choosing the right method will help the AI understand your intention more accurately.
| Strategy Type | Definitions and Objectives | Applicable Scenarios | typical example (Reasoning model applies) | Strengths and Risks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Command Driver | Directly give explicit steps or formatting requirements. | Simple tasks that need to be performed quickly | "Write the quick sort function in Python with comments on the output." | Accurate and efficient results / Limit the room for autonomous model optimization |
| demand-driven | Describe the context and goals of the problem, and plan a solution path from the model. | Complex problems requiring autonomous model reasoning | "I need to optimize the user login process, please analyze the current bottleneck and suggest 3 options." | Stimulate deeper reasoning in the model / Need to clearly define requirement boundaries |
| hybrid model | Combine the requirements description with the key constraints. | Balancing flexibility and control | "Design a three-day trip to Hangzhou that includes the West Lake and Lingyin Temple and is budgeted within $2,000." | Balance of goals and details / Need to avoid over-constraints |
| Inspired Conversations | Guiding the model's active thinking (the "why" and "how") through questioning | Exploratory questions, need models to explain logic | "Why do you choose gradient descent to solve this optimization problem? Please compare it with other algorithms." | Trigger model self-explanatory capacity / possible deviation from core objectives |
Different Situational Needs and Cueing Strategies
The way prompts are designed can affect the quality of AI responses in different usage contexts. Below are a few common types of requirements, with appropriate cueing strategies and examples.
| Mission Type | Applicable Models | Cue Focus | Example (valid tips) | Cueing Strategies to Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mathematical proof | inference model | Ask direct questions without step-by-step guidance | " Proof of the Pythagorean Theorem | Redundantly disassembled (e.g., "draw the diagram first, then the formula") |
| universal model | Show the requirement for step-by-step thinking and provide examples | " Derive the Pythagorean Theorem in three steps, ref: 1. Draw a right triangle... | Direct questions (easy to skip key steps) | |
| Creative Writing | inference model | Encourage divergence, set character / style | " Writing an Adventure Story in the Style of Hemingway | Excessive constraint logic (e.g., " time-ordered listing") |
| universal model | The need for clear targets to avoid free play | " Write a short story that includes "Quantum" and "Desert", no more than 200 words | Open-ended commands (e.g., " free creation") | |
| Code generation | inference model | Simple Requirements, Trusted Model Logic | " Implementing Quick Sort with Python | Step-by-step instructions (e.g., " write the recursive function first") |
| universal model | Step-by-step process to specify input and output formats | " Explain the principle of quick sort, then write the code and test the example | Fuzzy requirements (e.g. " write a sort code") | |
| Multi-Round Dialogue | inference model | Natural interaction, no need for structured commands | " What do you think the future holds for artificial intelligence? | Forced logic chains (e.g. " answer in three points") |
| universal model | Need to define the goals of the dialogue to avoid openness and fragmentation | " Analyzing the Future of AI from a Technical, Ethical, and Economic Perspective | Emotional questions (e.g., " Are you afraid of AI?") | |
| Logic Analysis | inference model | Throwing out complicated questions straight away | " Analyzing the Conflict Between Utilitarianism and Moralism in the "Trolley Problem" | Add subjective guidance (e.g., " What do you think is right? ") |
| universal model | Need to break down the questions and follow them step by step | " First explain the definition of the Trolley Troubles and then contrast the differences between the two ethical views | Ask complex logic questions at once |
How to express needs correctly with AI?
The key to getting AI to give accurate and useful responses lies in how clearly the requirements are expressed. Different types of requirements can be expressed in different ways. Below are the common types of requirements and the best prompting strategies.
| Demand Type | Features | Ways of Expressing Needs | Strategies for fitting inference-based models | Strategies to fit a generalized model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision-making needs | Need to weigh options, assess risks, and choose the best solution | Objectives + Options + Assessment Criteria | Requires logical extrapolation and quantitative analysis | Direct advice, relying on model experience generalization |
| Analyze demand | Requires deep understanding of data/messages, patterns or causal relationships | Problems + Data / Information + Methods of Analysis | Triggering Causal Chain Inference and Hypothesis Testing | Surface Summary or Classification |
| Creative Needs | Need to generate new content (text / design / proposal) | Theme + Style / Constraints + Creative Direction | Combining logical frameworks to generate structured ideas | Free diffusion and reliance on examples for guidance |
| Verification Requirements | Need to check for logical consistency, data reliability, or programmatic feasibility | Conclusion / Scenario + Validation Methodology + Risk Points | Self-designed verification paths and troubleshooting of conflicts | Simple confirmation, lack of in-depth deduction |
| Execution Requirements | Specific operations to be completed (codes / calculations / processes) | Code / Calculation Requirements + Output Format | Self-optimizing steps for efficiency and accuracy | Strictly according to instructions, no autonomous optimization |
Examples of AI prompts
When using AI, it is clear and unambiguous that Prompt It can improve the accuracy and usability of AI responses. Here's howPractical Tips and ExamplesIt helps you learn how to design the best prompts for different needs, so the AI understands your requests more accurately.
Decision Need: Let AI Provide Comparison and Evaluation
- Practical Tips: "There are two options to reduce logistics costs:
- Create your own regional warehouse (high initial investment, low long-term cost)
- Work with third parties (pay-as-you-go, high flexibility)
- Please recommend the best option based on the ROI calculation model against the total cost over a 5-year period."
Analyzing Needs: Data Analysis and Trend Forecasting
- Practical Tips: "Analyze the sales volume data of new energy vehicles (with CSV) for the past three years:
- Growth trends and policy relevance;
- Forecasting market share in 2025 requires the use of an ARIMA model and an explanation of the basis for parameter selection."
Creative Demand: Generating Content, Copy and Ideas
- Practical Tips: "Design a smart home product that focuses on:
- To address the safety of elderly people living alone;
- Combine sensor networks and AI alerts;
- Prototype sketches illustrating three different technology paths are provided."
Verification of needs: Confirmation of program feasibility
- Practical Tips: "The following is the conclusion of a paper: 'Neural network model A is better than traditional method B', please verify it:
- Whether the experimental data support the conclusion;
- Check for deviations in the control group settings;
- Recalculate p-values and determine significance."
Execution Requirements: Generate specific content, such as program code, calculation results.
- Practical Tips: "Convert the following C code to Python, required:
- Holding time complexity remains unchanged;
- Use numPy to optimize array operations;
- Output complete code with time test cases."
Extended Reading:DeepSeek V3 model: the strongest open source AI, 18 technology highlights, a must-have for AI players!
Should I learn cues or not? What are cues?
Prompts are user inputs to the AI instructions or information from the system to allow the AI to produce a specific output or perform a specific task.
Simply put, the cue is our way of communicating with the AI. Conversation.The language used can be a simple question, a clear instruction, or a complex task description.
Basic Structure of Prompts
A valid prompt should containInstructions, Context and ExpectationsThree core elements that ensure AI understands and responds accurately:
- Instruction
- This is the heart of the prompt, directly telling the AI what you want it to do.
- For example, "Please help me write a 500-word essay on the topic of environmental protection."
- Context
- Provides additional contextual information to help the AI understand and perform tasks more accurately.
- For example, "The target audience for this article is college students who want to present it in plain language."
- Expectation
- Specify your requirements and expectations for the AI response, such as output format, tone, or detail requirements.
- For example, "Please use a bulleted list of three environmental actions and provide specific benefits for each."
Prompts Operation Procedure
The operation of the prompt can be divided into the following steps:
- User input prompt → Clearly describe tasks and needs
- AI Parsing Command → Process according to the content of the prompt.
- AI Generation Output → Provide eligible results
Cue Type
- Command prompts: Directly tell the AI what tasks it needs to perform.
- Question & Answer Prompts: Ask the AI a question and expect an answer.
- Role-playing Prompts: Ask the AI to play a specific role and simulate a specific scene.
- Creative Tips: Lead AI for creative content generation.
- Analytical Cues: AI is required to analyze and reason about the given information.
- Multimodal Cues: Combine text, image, and other forms of input.
The Nature of Cues
| special feature | descriptive | typical example |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Bridge | Connecting Human Intent and AI Understanding | "Translate the following into French: Hello, world." |
| context provider (computing) | Providing the necessary background information for AI | "Suppose you were a 19th-century historian commenting on the rise of Napoleon." |
| Task Definers | Clearly describe what the AI needs to accomplish. | "Write a 200-word introduction to an article about climate change." |
| Output Shaper | Influencing the Form and Content of AI Outputs | "Explain quantum mechanics in simple terms, assuming you're talking to a 10-year-old." |
| AI Capability Navigator | Directing AI to specific skills | "Use your creative writing skills to create a short story about time travel." |
Extended Reading:The five basic rules of deepseek and the basic use of the process!
Mastering Cue Design: Essential Core Skills for the AIGC Era
In the era of rapid development of AIGC (Artificial Intelligence Generated Content), Prompt Engineering has become a key factor affecting the quality of AI output.
Precise and efficient prompts can guide AI to produce more responsive results, improving the quality of content creation, data analysis and smart applications.
These are discussed and listed belowCore Skill Set for Prompt DesignandAdvanced SkillsThe AIGC program is designed to help you master the key competencies of the AIGC era.
Core Skill Set for Prompt Design
In AIGC applications, cue design involves a number of key capabilities that cover the complete process from problem construction to result optimization.
| core skill | subitem (of program) |
|---|---|
| Problem Building Capability | - Transform complex, ambiguous human needs into structured AI tasks - Identify the key core elements and constraints of the problem - Designing clear and precise cue structure |
| Creative Leadership | - Designing Cues to Inspire Creative Thinking in AI - Expanding AI output possibilities with analogies, reverse thinking, and other techniques - Skillfully combining concepts from different fields to generate cross-boundary innovations |
| Result Optimization Capability | - Analyzing AI Output to Identify Room for Improvement - Optimize output quality by iteratively adjusting prompts - Design evaluation criteria to quantify the effect of the cues |
| Cross-domain integration capabilities | - Translating areas of expertise and knowledge into effective prompts - Bridging Different Science and AI Capabilities with Cues - Creating Cross-Disciplinary Solutions for Degradation |
| Systems Thinking | - Designing a Multi-Step, Multi-Dimensional Cueing System - Structuring the cue template library for efficiency and consistency - Developing cueing strategies for complex scenarios |
Mastering these core skills can effectively improve the output accuracy and controllability of AI, further enhancing the value of applications.
Cue Design Advanced Skills
With the evolution of AIGC technology, cue design requires not only accuracy and structure, but also a higher level of cognitive and creative ability.
| core skill | subitem (of program) |
|---|---|
| contextual understanding | - In-depth analysis of mission context and implicit needs - Consideration of cultural, ethical and legal factors - Anticipating possible misunderstandings and boundary conditions |
| abstracting ability | - Identify generic patterns to improve reusability of prompts - Design flexible, scalable templates for prompts - Creating cues for different scenarios |
| critical thinking | - Objectively evaluate AI outputs to identify potential biases and errors - Designing Counterfactual Cues to Test AI Depth of Understanding - Constructing a validation mechanism to ensure the reliability of AI outputs |
| Innovative Thinking | - Explore unconventional cueing methods - Combining the latest AI research results to expand the application boundary - Designing Experimental Cues to Drive the Evolution of AI Capabilities |
| Ethics | - Embedding Ethical Considerations in Prompts - Designing fair and inclusive AI interaction models - Preventing and mitigating the possible negative impacts of AI |
The core skill set of cue design not only covers technical expertise, but also emphasizes the importance of cognitive ability, creative thinking and soft skills.
These core skills form the basis of prompt design, covering the entire process from problem analysis to idea generation to optimization of results.
Contextual understanding enables designers to work in complex social and cultural contexts; abstraction skills help to increase productivity and expand the range of applications.
Critical thinking is the key to ensuring the reliability and fairness of AI applications; the ability to think creatively pushes the boundaries of AI applications, while ethical awareness ensures that AI development is consistent with social values.
The DNA of Prompts: Analyzing the Basic Elements of a Strong Prompt Categorization
The basic elements of a cue can be categorized into three main groups based on their functions and roles:Information type elements, structure type elementsrespond in singingControl Class ElementsThe
- Information Class Elements: Determines the specifics of what the AI needs to deal with in the generation process, including subject matter, context, data, etc., providing the AI with the necessary knowledge and context.
- structural class element: Used to define the type of organization and presentation of the generated content, which determines the structure, format and style of the AI output.
- Control Class Elements: Used to manage and guide the AI generation process, ensuring that the output meets expectations and enables necessary adjustments, it is an essential tool for realizing advanced cue engineering.
Cue Element Combination Matrix
| Objectives | Key Impact Elements | Elements of secondary impact | Combination effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved output accuracy | Theme element + Data element + Quality control element | Knowledge Domain Element + Output Validation Element | Ensure that AI generates content based on accurate subject matter and data, and improves accuracy through rigorous quality control and validation |
| Enhancing Creative Thinking | Theme element + Background element + Constraints element | Reference Element + Iterative Instruction Element | Stimulate AI's creative thinking by providing rich background information and appropriate constraints, while promoting innovation through multiple rounds of iteration. |
| Optimize task execution efficiency | Task command element + Structure element + Format element | Length element + Style element | Improve execution efficiency through clear task instructions and predefined structures, while ensuring output meets specific format and style requirements |
| Improve output consistency | Style Element + Knowledge Domain Element + Constraints Element | Formatting elements + quality control elements | Ensure consistency of output through harmonization of individual bees and areas of expertise and knowledge while maintaining standards using constraints and quality control |
| Enhanced Interactive Experience | Iterative Command Element + Output Validation Element + Quality Control Element | Mandate Element + Background Element | Creates a dynamic interaction model that allows the AI to validate and optimize itself while flexibly adjusting its output to the task and context. |
Cue Element Synergistic Effects Theory Core Concepts
- Complementary enhancements: Certain combinations of elements can complement each other to produce a 1+1>2 effect, improving the accuracy of AI comprehension and output.
- Cascade Activation: The activation of an element may trigger a chain reaction of related elements, forming a positive loop of optimized cues.
- Conflict Reconciliation: The interaction of certain elements may create unexpected limitations or effects, and therefore need to be balanced and tested.
- Emerging Properties: Certain combinations of elements can be applied to a wide range of scenarios, increasing the flexibility and adaptability of the prompts.
Tips for Tuning AI: The Key to Improving Cueing Effectiveness
Want AI to generate more accurate content? Master these five strategies to boost your cueing results and make AI smarter and more efficient!
Strategy 1: Define tasks precisely to reduce ambiguity
- Identify the core issues and ensure that instructions are specific and clear
- Remove unnecessary information to prevent AI from generating irrelevant responses
Strategy 2: Decompose complex tasks appropriately to reduce the cognitive burden on AI.
- Split the task into multiple steps and generate them step-by-step in segments
- Designing logical chains to make AI easier to understand
Strategy 3: Introduce Guiding Questions to Enhance the Depth of Generated Content
- Setting up multi-level problems to allow AI to think from multiple perspectives
- Promote AI comparisons or arguments to produce deeper and more varied responses
Strategy 4: Controlling Prompt Length to Ensure Accuracy of Generation
- Avoid too long or too short commands and keep them at the right length.
- A clear step-by-step guide for AI can be provided to prevent biased responses.
Strategy 5: Flexible Use of Open and Closed Cues
- Open Cue: Ask open-ended questions that allow AI to generate content from different perspectives and stimulate creativity.
- Closed Tip: Provide specific questions or set explicit limits and ask the AI to give precise answers.
With these strategies, you can guide your AI more effectively, improve the accuracy and depth of generated content, and make your AI smarter!
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions of Cue Design for Beginners
In the AIGC era, cue design is a key technology that affects the quality of AI output.
However, many novice designers often fall into some common pitfalls due to their inexperience when designing prompts, resulting in less than optimal results.
Below is a list of these common mistakes and effective strategies to help users improve the accuracy and applicability of their prompts.
1. Lack of iterative traps (expecting perfect results all at once)
- Trap condition
- Overly complex initial prompts.
- Abandon unsatisfactory output rather than analyzing the problem and adjusting the prompt.
- Lack of systematic feedback and analysis of AI results.
- Response Strategy
- Adoption of the incremental adjustment method: Start with the basic prompts and gradually add details and requirements.
- Active Leadership AI: Ask them to explain their reasoning for self-assessment and provide suggestions for improvement based on these explanations.
- Prepare for multiple conversations: Design a sequence of follow-up questions to help clarify the content and optimize the initial output.
2. Over-command and vague-command traps (when details are overloaded or the intent is unclear)
- Trap condition
- Cues that are too simple or too cumbersome and lengthy make it impossible for the AI to accurately understand the requirements.
- AI Outputs Fall Woefully Short of Expectations
- Frequent changes to the cue without really identifying the need resulted in erratic output.
- Response Strategy
- Balance Detail: Provide sufficient context, but avoid being overly restrictive.
- Identify key points: Highlight the most important 2 to 3 requirements.
- Use structured formatting: Use a clear structure to organize requirements.
- Examples: If possible, give a short example of the desired output.
3. Hypothetical bias trap (when the AI only tells you what you want to hear)
- Trap condition
- Prompts that contain obvious positions or tendencies that bias the AI output.
- Most of the information provided is in support of a particular viewpoint.
- There is a lack of presentation of opposing or opposing viewpoints.
- Response Strategy
- self-examination: Reflect on your possible biases when designing prompts to ensure objectivity in question design.
- Use neutral language: Avoid biased or suggestive wording in the prompts, and make sure the questions are open-ended and free of preconceived notions.
- Requires multi-perspective analysis: AI is explicitly required to provide a comparative analysis of different perspectives, rather than a unilateral conclusion.
- critical thinking: Be skeptical of AI output and cross-check important information to ensure accuracy.
4.Hallucination Generation Trap (when the AI confidently babbles)
- Trap condition
- Specific data or facts provided by AICannot be verifiedIf you do not have a copy of the document, you may not be able to read it.
- AI outputs contain terms or concepts that seem specialized but don't actually exist.
- AI is given for future or uncertain events.Too specificThe forecasts made by the Company are misleading.
- Response Strategy
- Request Data Source: Ensure information credibility by allowing AI to answer questions with specific data or authoritative explanations.
- Fact checking: Require AI to distinguish between verified facts and speculative content to avoid uncertain information being treated as a definitive conclusion.
- Multi-Confirmation: AI is required to provide multiple perspectives or cross-checked data sources to improve accuracy.
- Simplified Guidelines: AI is explicitly required to provide simple, clear facts, avoid over-extension or unfounded speculation, and make the results easier to understand and validate.
5. Ignoring the Ethical Boundary Trap (Underestimating the Ethical Limits of AI)
- Trap condition
- Asking the AI to generate content that is controversial, unethical, or illegal causes the AI to refuse to respond or output ambiguous results.
- Confused or dissatisfied with the AI's refusal to respond
- Attempts to ignore or bypass the ethical and security constraints of AI.
- Ignoring the potential ethical implications of AI output results in content that may pose a risk.
- Response Strategy
- Understanding the Boundary: Familiarize yourself with the ethical rules and limitations of AI systems to avoid designing unorthodox prompts.
- Suitable Expression: Ensure that your request complies with legal and ethical standards.
- Ethical clarity: Include ethical considerations and contextualize information explicitly in prompts to ensure that output is compliant.
- Impact Assessment: AI is required to assess the potential social impact of its output to ensure that the information is not misleading or harmful.
- AI Ethical Considerations
- Privacy
- Equity and non-discrimination
- Transparency and Interpretability
- Social Impact Assessment
- Safety Compliance and Abuse Prevention
Cue Design Checklist
When designing your prompts, you can use the following checklist to ensure that the content is up to standard and to avoid common mistakes:
- Clarity of Purpose
- sufficiency of information
- Structural Rationality
- Language Neutrality
- Ethical Compliance
- Verifiability
- Iterative Space
- Output Format
- Medium Difficulty
- Diversity considerations
These elements can be used as a standard framework for the design of cues to ensure that AI can produce expected, compliant, and safe output content. Through proper ethical design and review mechanisms, AI can be maximized while minimizing risk and ensuring that the application of the technology meets social and ethical standards.
Enhancing AI Creativity: Using Reverse Thinking and Open Cue Designs
When designing AI cues, innovation and flexibility are key factors in improving the quality of the output.
However, many novices tend to fall into too much one-dimensional design thinking, limiting the creativity and diversity of AI.
The following is a discussion ofTapping into Reverse Thinkingrespond in singingFlexible use of task opennessTwo strategies to help users optimize cue design and enhance AI performance.
Tapping into Reverse Thinking: Approaching from a Non-Traditional Perspective
- Innovative design strategies:
- Designing reverse tasks: prompts can guide the AI to approach a problem from the opposite perspective, providing content that is different from what is traditionally generated and facilitating divergent thinking.
- Challenging the default mindset: Challenging conventional settings that are bound by tasks, prompting the AI to generate challenging and innovative content.
Flexibility in Task Openness: Giving AI the Freedom to Play
- Innovative design strategies:
- Set up a basic framework with room for exploration: prompts should provide a structured framework that includes specific generative goals, but should not be overly restrictive in terms of expression or detailed content to ensure that the AI has sufficient room for creativity.
- Multi-dimensional task guidance: By guiding the AI to look at problems from multiple perspectives, the AI will be inspired to think diversely about the generated content, thus enhancing the richness and novelty of the output.
Using these strategies, novices can avoid making AI outputs too monotonous or stagnant, and further realize the potential of AI for creative thinking and flexible expression.
With proper cue design, AI can provide more inspiring, diverse, and high-value outputs.
AI Flaws: Fictitious Words and Opportunistic Illusions
AI Hallucinations. This refers to the fact that when AI generates text or answers questions, although the syntax appears to be reasonable and well-organized, the actual output may be completely fictitious, does not match the facts, or even carries incorrect or misleading information.
Reasons for formation
AI illusions often stem from models relying on probabilistic choices to generate content in the absence of relevant information, rather than real-world knowledge and reasoning.
As a result, such output may give people an impression of credibility, but it does not tally with the facts and may even mislead users.
In addition to knowledge deficiencies, potential drawbacks and limitations of AI include interpretability, computational costs, data bias, real-time updates, data security, personal privacy, and malicious outputs.
AI Illusion: Five Types of Mistakes and Seven Characteristics
Artificial intelligence may experience different types of hallucinations during the content generation process, and these errors may affect the accuracy and reliability of the results. We can learn from theFive main typesandSeven wrong featuresTo understand the causes and manifestations of AI hallucinations.
Five Types of AI Illusions
| Type of hallucination | Data Availability | Depth of understanding | Speech Accuracy | Ability to integrate external information | Logical reasoning and abstraction | Typical Errors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Misuse | Data available | lower (one's head) | your (honorific) | your (honorific) | center | Uses known data, but some answers are not detailed or are incorrect |
| Language Misunderstanding | Data available | your (honorific) | lower (one's head) | your (honorific) | center | Misinterpretation of the context of the question and answers may be off-topic |
| missing information | No data | center | lower (one's head) | lower (one's head) | center | Inability to accurately retrieve or integrate external information |
| Reasoning Error | Selected Data | your (honorific) | your (honorific) | center | lower (one's head) | Flawed reasoning or false assumptions |
| create something from nothing | No data | lower (one's head) | center | lower (one's head) | lower (one's head) | Generate completely fictitious information out of thin air without data support |
Seven Characteristics of AI Hallucinations
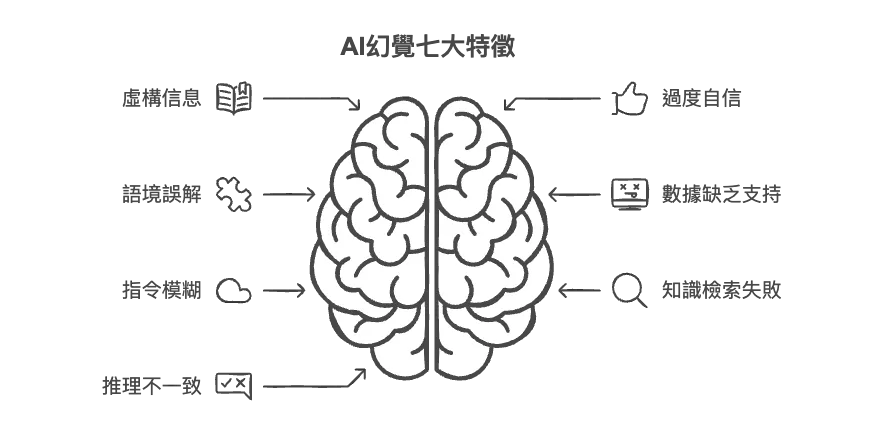
- Fictitious Information
- AI generates information that is not true or does not exist.
- When there is a lack of literature support, the model may fabricate data or facts.
- Overconfidence
- AI can give "sure" but wrong answers in some cases.
- Users may be under the mistaken impression that the AI's response is always correct.
- Language Misunderstanding
- The AI may not fully understand the context of the conversation.
- Certain complex questions may result in answers that do not match user expectations.
- Lack of data support
- AI-generated content may lack reliable data sources.
- The data in the response may not be verifiable or traceable.
- ambiguity of instructions
- The AI may produce biased responses when the instructions are not clear enough.
- may misinterpret the user's intent and result in answers that do not meet expectations.
- Knowledge Retrieval Failed
- AI cannot guarantee that all information is based on the most up-to-date knowledge base.
- There may be instances where current or accurate information cannot be found.
- Inconsistent reasoning
- AI may produce contradictory answers during the reasoning process.
- Different but conflicting answers may be given to the same question.
Conclusion
DeepSeek is an AI generation tool that can help users accomplish various tasks such as text creation, semantic analysis, and code generation. By understanding the characteristics and applications of AI models, you can improve your experience and work efficiency.
With the development of AI technology, how to rationally utilize such tools will become one of the most important ways to enhance productivity and creativity.